Color accuracy is important for the quality of your TV picture. It shows how accurately your TV reproduces colors compared to real life. While minor color differences may go unnoticed, significant inaccuracies can be distracting. However, you should know that no TV can achieve perfect color reproduction.
Color accuracy explained
Color accuracy measures how accurately a display reproduces colors compared to reference or expected values. Simply put, it measures how “correct” and “realistic” the colors on the screen look compared to their original or standardized versions.
An example of inaccurate color reproduction:

Modern TVs, especially mid-range and high-end models, can often be calibrated to achieve near-perfect color accuracy. However, you will not always want to do calibration on your own. Most users expect good color accuracy when they buy and install the device, so it’s worth paying attention to this setting when choosing. TVs also have settings that allow you to change the gamma or color tone, thereby correcting the color reproduction.
Benchmark: For a color to be considered accurate, there must be a benchmark – a standard for comparison. The reference can be a tangible object (such as a red apple) for a close enough comparison, or an industry-accepted digital color standard against which adjustments are usually made.
Deviation: If the apple appears orange instead of red on the display, this represents a deviation from the “true” color, referred to as a color error.
Why it’s important: Imagine editing a photo on a screen with poor color reproduction. The printed image might look significantly different from what you saw on your monitor. Similarly, watching a movie on a screen with inaccurate color reproduction can change the perception of the visual content.
How do other color parameters impact color accuracy?
Color gamut: The range of colors a display can reproduce.
Here’s a color range in RGB format; triangles show Rec.709, DCI-P3, and Rec.2020 color ranges:
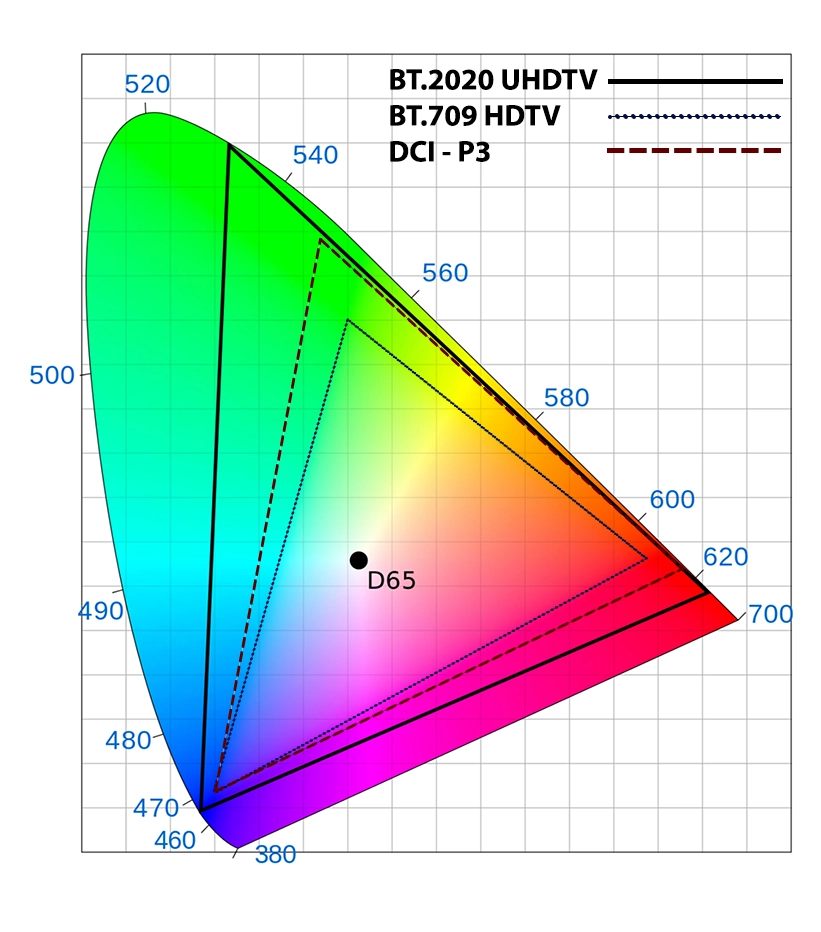
- A wider color gamut allows a display to reproduce a broader spectrum of colors. However, just because a display can show more colors doesn’t mean it will show them accurately.
- If a display claims to cover 100% of the DCI-P3 color gamut but has poor color accuracy, the colors within that gamut might not match the reference colors of the standard.
- Contrast: it’s actually quite difficult to measure, but basically it shows how much brighter the light part of the image is compared to the dark part.
- A higher contrast ratio allows for more distinguishable shades between the extremes, leading to richer and more detailed images.
- If the contrast ratio is poor, subtle color differences might get lost, impacting the accuracy of color reproduction. For instance, shadow details in a dark scene might merge into a single indistinct blob.
- Color Depth: The number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel. Common depths include 8-bit (256 colors), 10-bit (1,024 colors), and 12-bit (4,096 colors). Since our eye can catch around 10 million colors, even 8-bit (that’s around 16 million colors)
- Color depth determines the granularity of color representation. Higher bit depths allow for smoother gradients and transitions, reducing banding effects.
- A display with higher color depth can represent subtle color variations more accurately. For instance, a sunset might appear as a smooth gradient on a 10-bit display but show visible banding on an 8-bit one.
- Color temperature and color accuracy: Color temperature, measured in Kelvin (K), describes the hue of a light source within a display. It’s a spectrum that ranges from warm (reddish) to cool (bluish) tones.
- Warm Tones (Low Kelvin Values, 2700K – 3500K): These tones are reminiscent of the glow from incandescent bulbs, producing a cozier, more relaxed viewing experience.
- Cool Tones (High Kelvin Values, 5500K – 6500K): These tones resemble daylight, offering a crisper and more alert viewing ambiance.
| Color Temperature | Description |
|---|---|
| < 2700K | Ultra-Warm |
| 2700K – 3500K | Warm |
| 3500K – 4500K | Neutral |
| 4500K – 5500K | Cool |
| > 5500K | Ultra-Cool |
Color accuracy and panel type
The type of panel plays a huge role in image quality and especially in the quality of color reproduction. The leader in this area is undoubtedly OLED panels. As for LED screens, it all depends on the quality of the materials used and the production technology. There are LED panels of low quality, and it does not matter whether they are made by IPS or VA technology. There are LED panels made on outdated lines using cheap matrices that have mediocre color rendering, and there are panels made using materials on quantum dots, the so-called QLED-displays, here they can have a pretty good color rendering quality.
Does HDR affect color accuracy?
HDR can significantly affect color accuracy on TVs. HDR is a technology that enhances the visual experience by expanding the range of brightness, contrast, and color compared to standard dynamic range (SDR) content. While HDR can improve the overall visual quality, it also introduces new challenges and considerations related to color accuracy.
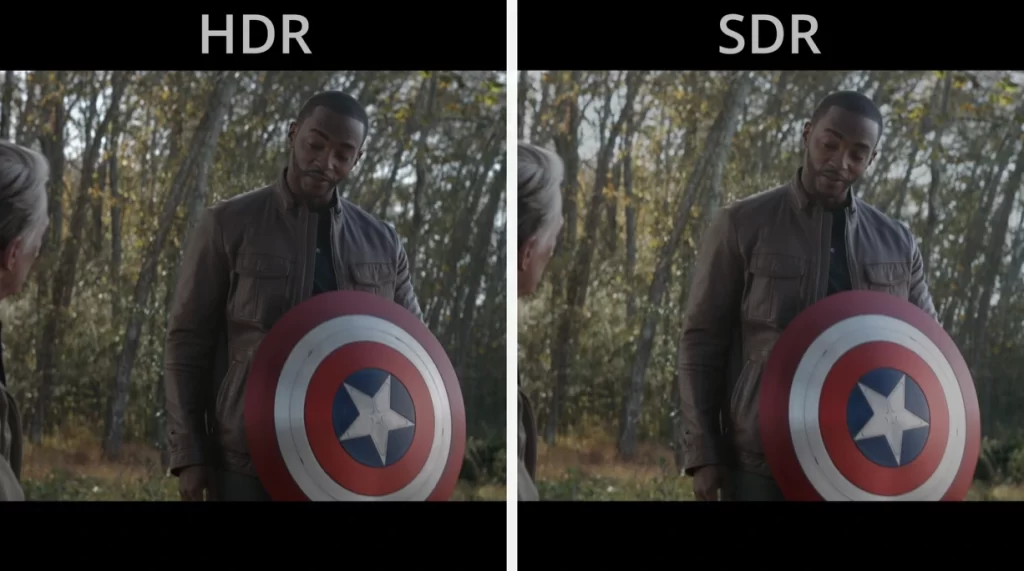

HDR content often utilizes a wider color gamut, closer DCI-P3 or even beyond, but no current TV model can reach Rec. 2020 color range compared to the standard sRGB color gamut used for SDR content.
This expanded color range allows for more vibrant and saturated colors that can better mimic real-world colors. However, to maintain accurate color representation, a TV must be capable of reproducing these extended color ranges correctly.
In conclusion:
The color accuracy of a TV or monitor depends on many factors, ranging from the quality of the panel itself to the image processing software on the TV or monitor. In fact, no budget or mid-range TV or monitor can provide color reproduction that meets the standard. That’s why TV manufacturers never talk about color accuracy, even if the TV is high-end, the most you can learn is that it covers the range of a certain standard.
Since OLED TVs are able to show the most correct colors, Samsung’s 2024 OLED TVs are Pantone certified. Here’s what Samsung says (Discover pure blacks, bright whites and Pantone-validated color with OLED Technology). But it confuses me that Pantone colors were mainly developed for printing and use 4 or 7 colors to create color, but TVs and monitors create color from 3 colors. So the color may correspond to Pantone but whether it will correspond to DCI-P3 I do not know.