Today, LG stands as a colossal conglomerate, with its influence sprawling across numerous sectors. It is particularly renowned for its cutting-edge TVs, home appliances, air conditioners, and laptops, which have consistently set industry standards. Although LG’s product line once extended to phones and tablets, a challenging period marked by three consecutive years of financial losses compelled the company to make a strategic withdrawal from this segment of the market.
To get a clear picture of LG Corporation’s development and wide-ranging skills over the years, we need to start by looking at how the company is organized into different business divisions. This detailed view helps us understand the steps LG has taken, the variety of areas it has branched into, and the depth of its knowledge. Each division, with its specific companies and areas of focus, has been key in building LG’s reputation and success.
LG’s business by division
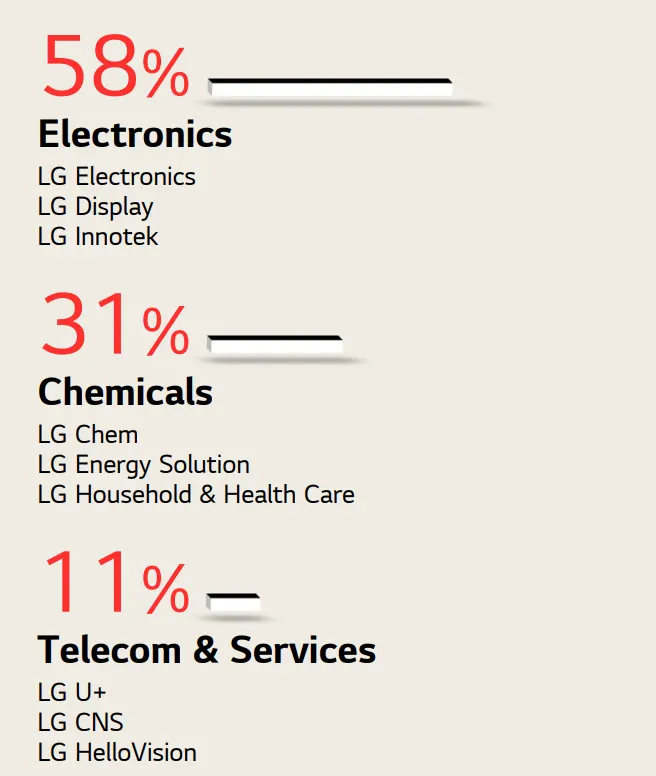
LG has three business areas: electronics, chemicals, and telecommunications. Each business line has its own companies that are responsible for certain production.
LG Electronics Division
58% of the percent brings the electronics manufacturing business line. This business line includes the following companies:
- LG Electronics: this company is engaged in manufacturing
- Liquid crystal and OLED televisions
- Audio equipment
- Home appliances
- Computer monitors, laptops, components
- Air conditioners and air filtration systems
- Energy-saving products, such as solar panels
- Business products such as video surveillance systems and industrial monitors
- Refrigeration equipment
- LG Display: the company manufactures various displays for phones and televisions.
- LG Innotek: manufactures electronic components from cameras for phones and backlit displays to microchips.
LG Chemical Division
31% of the company’s revenue comes from the chemical industry, which is one of the company’s core businesses.
- LG Chem: Petrochemicals, production of plastics, polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, acrylics, synthetic rubber, alcohols, etc.
- Energy solutions: batteries for portable devices and electric vehicles.
- Advanced Materials: automotive components, LCD and battery materials, organic LEDs.
- Pharmaceuticals: growth hormones, vaccines, anti-diabetic drugs.
- Other: agrochemicals (pesticides, fertilizers, seeds) and other activities.
- LG Energy Solution: production of large batteries, including for automobiles.
- LG Household & Health Care: production of consumer goods, cosmetics, household products and beverages.
LG Telecom & Services Division
11% of revenue comes from the Telecom & Services division, which includes the following companies
LG U+: the company provides cell phone services in Korea.
LG CNS: the company provides information technology services, including consulting, systems integration, network integration, business process outsourcing, and information technology outsourcing.
LG HelloVision: LG HelloVision (“LGHV” or the “Company”) is the largest multi-system cable television operator (“MSO”) in South Korea with over 4 million subscribers.
LG Corporation History from 1947
Founded in 1947 as Lak-Hui Chemical Industrial Corp., LG has come a long way from its roots in South Korea. The company began as a chemical company, producing cosmetics and industrial materials. Over the years, LG has diversified its business to adapt to market trends and customer needs.
The Decade from 1950 to 1960 at LG
In the 1950s, LG made a move that shaped its future as an electronics giant. The company ventured into plastics manufacturing, a strategic decision that later proved invaluable in entering the consumer electronics market. The plastics division produced products such as combs and containers, an important step towards technological innovation.
The real turning point came in 1958 when the company, renamed GoldStar, produced the first radio receiver. This achievement was more than just a technological advancement, it marked South Korea’s entry into the electronics era and laid the foundation for LG’s transformation into a world-renowned company.
The period 1960-1970 at LG
The 1960s and 1970s were pivotal decades in LG’s history, transforming it from a local player to a global giant in consumer electronics. During this time, the company, then known as GoldStar, began to develop many new products and technologies that significantly expanded its presence and laid the foundation for the diverse product portfolio it boasts today.
One of the most important milestones of this period was the production of South Korea’s first black-and-white television in 1966. This was not only a technological achievement but also a symbol of South Korea’s growing potential in electronics. The television was not just a product but the epitome of social progress, allowing the South Korean people greater access to information and entertainment.
In 1967, a year after bringing television into homes, LG made a pivotal move by stepping into the telecommunications world with the founding of GoldStar Communications. This move broadened the company’s range of products and services. Initially, LG focused on producing telephone sets and switches, gradually progressing to more sophisticated systems and wireless communication infrastructure. This strategic entry into the telecommunications field proved to be a wise decision, as the industry soon became one of the most vital and rapidly growing sectors globally.
1970 marked another significant milestone for LG, as it ventured into the air conditioning sector, introducing South Korea’s first air conditioner. This achievement not only added to LG’s list of pioneering accomplishments but also enriched its assortment of home appliances.
To support its expanding product lineup, LG channeled resources into research and development (R&D) and boosting production capabilities. During this era, new factories and R&D centers were established to stay in stride with technological advancements and cater to a wider consumer base. These investments were crucial for sustaining a competitive edge and set the stage for LG’s future ventures into more advanced technological realms.
In these crucial decades, LG also started to reach out beyond its home turf of South Korea, aiming to make a mark on the global stage by exporting its products to various countries. This international expansion was a critical step for LG, helping the company to understand and adapt to the preferences of consumers worldwide, ultimately solidifying its position as a global electronics powerhouse.
In summary, the decade from 1960 to 1970 was a period of transformation and growth for LG. The company branched out into new sectors, innovated its product line, and laid the foundational steps toward becoming a leading figure in the global electronics and telecommunications industries. It was a time marked by innovation, expansion, and significant progress, pivotal in shaping the LG we recognize today.
LG’s Decade of Progress: Reflecting on 1970-1980
The 1970s and 1980s marked yet another transformative phase for LG, which was operating under the GoldStar brand at the time. Building on the success of the previous decade, the company aimed to further innovate, broaden its range of products, and establish a stronger global presence. This period was characterized by numerous firsts, the initiation of new ventures, and strategic moves that solidified LG’s standing in the electronics world.
A major highlight of this era was LG’s foray into the home computer market. In 1977, the company unveiled South Korea’s first color TV, followed by the country’s inaugural color computer monitor in 1978. By venturing into the computer monitor sector, LG not only expanded its product lineup but also tapped into a burgeoning market poised for significant growth. Computers were rapidly becoming essential in business, education, and, eventually, households. LG’s entrance into this field represented a forward-thinking approach to cater to the needs of a tech-savvy clientele.
But LG’s ambition extended beyond monitors. In the late 1970s, the company delved into semiconductor technology, establishing a dedicated research and production facility for semiconductors. Given that semiconductors are crucial components of electronic devices, this move was strategically important. It allowed LG to oversee the entire lifecycle of its products, from the raw materials to the finished goods.
LG’s efforts during this time weren’t limited to products and technology; the company also sought to enhance its international footprint. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, LG actively exported items like TVs, radios, and air conditioners to various countries outside of South Korea. By 1978, the company’s export earnings reached $100 million, which is roughly equivalent to $400 million in today’s money.
Furthermore, this period saw LG place a strong emphasis on quality and research. Significant investments were made in research and development to boost the company’s innovation capacity.
To sum it up, the 1970s and 1980s were crucial years of advancement for LG. The company branched out into new, rapidly growing sectors like computer monitors and semiconductors, while also extending its reach globally and laying down a solid foundation for future growth through research, technology, and international expansion.
A Decade of Dynamics: LG from 1980 to 1990
During this decade, the company redoubled its efforts to become a technology leader and global brand. Significant investments in research and development, a focus on quality, and successful entry into new and emerging markets marked this period.
One of the defining moments of the decade was GoldStar’s focus on advanced technology. In 1987, the company began manufacturing videocassette recorders (VCRs), targeting the booming home entertainment market. VCRs became an integral part of homes around the world, changing the way people watched movies and television shows. Entering this market was another example of LG’s ability to understand consumer behavior and needs.
LG also strengthened its telecommunications activities during this decade. The previously established telecommunications division, GoldStar Communications, expanded its portfolio to include wireless technologies. This gave the company a strong foothold in the telecommunications boom in the following years.
The 1980s were also important in terms of global expansion. After establishing its first overseas manufacturing facility in the United States in 1982, the company continued to expand its international presence. It entered markets in Europe and other parts of Asia, signaling its intention to become a global brand. The decision to go international was not only about sales but also about understanding different markets and adapting products to specific local needs.
The period 1990-2000 at LG

After entering global markets, the Gold Star brand was no longer perceived as unique but was drowning in a sea of similar brands. The company decided to rebrand globally with a strong advertising campaign. The rebranding of GoldStar to LG Electronics in 1995 prepared the company for an era of rapid globalization and technological innovation. The decade was marked by a series of calculated risks, ambitious undertakings, and groundbreaking achievements that further strengthened LG’s position in the industry.
One of the most important developments during this period was LG’s focus on digital technology and the development of home appliances. This was greatly facilitated by the collapse of the USSR and the opening of markets in Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union, home to some 500 million people. Who were eager to buy electronics and home appliances. In 1997, LG introduced the DIOS (Digital, Intelligence, Optimization, and Sensing) refrigerator, taking a familiar household appliance and adding innovative digital features. The DIOS line demonstrated LG’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of home appliances and underscored the company’s investment in advanced technology.
In 2000, LG made its mark by developing the world’s first Internet-connected refrigerator. Although the product was not immediately commercially successful – the Internet was in its infancy – it was an essential indication of LG’s forward-thinking approach. It offered a glimpse of a future where smart homes would become the norm and appliances would become connected and intelligent.
This period also marked LG’s entry into the highly competitive mobile phone market. Not being the first in the market, LG invested heavily in producing functional and stylish mobile phones. This move was aimed not only at expanding the product line but also at positioning LG as a lifestyle-oriented brand.
Research and development remained a cornerstone of LG’s strategy. In the 1990s, the company increased its investment in R&D, focusing on technologies that would enable the next generation of electronic devices.
The 2000-2010 LG’s era
The turn of the century was a dynamic time for the technology industry, with the proliferation of the Internet, the advent of smartphones, and an increasing focus on innovative, connected devices. LG was not just a bystander during these transformative years but an active participant, shaping trends and setting standards.
One of the defining moments of the decade for LG was its pioneering work in display technology. In 2004, the company launched the world’s first 55-inch LCD TV, setting a new standard for home entertainment. A year later, in 2005, LG went one step further by introducing the world’s first 71-inch 3D plasma TV. These innovations were not just about more giant screens or more features; they were about enhancing the viewing experience for the consumer.
The 2000s were also significant for LG’s mobile phone business. The company attracted attention with stylish and feature-rich phones such as the Chocolate and Shine. But the most iconic was the LG Prada, launched in 2007. Developed in collaboration with Italian fashion house Prada, the phone was one of the first mobile devices to feature a capacitive touch screen. It combined style with functionality and served as a precursor to the sleek, touch-based smartphones that would dominate the market in the future.
The period 2010-2020 at LG
The decade from 2010 to 2020 was both a triumph and a challenge for LG, reflecting the complexities of a rapidly changing technology landscape. Chinese companies emerged to supply markets with low-cost electronics. And so the TV market changed globally. Japanese companies failed, ceding international markets to Korean and Chinese companies. Brands such as Philips, Sanyo, Toshiba, and Sharp stopped making TVs and leasing their brands to other companies.
One of the most notable achievements of this decade was LG’s work in OLED technology. In 2012, LG introduced the first 55-inch OLED TV, demonstrating incredibly vivid colors and deep blacks. This was a prototype; OLED panels were still imperfect at the time. It took LG another four years for OLED TVs to become a mainstream product.
LG has also made significant progress in the home appliance market. In 2017, the company launched the SmartThinQ platform, which allows users to control various LG appliances through a single app. From washing machines that can self-diagnose malfunctions to refrigerators that suggest recipes based on their contents, LG has been at the forefront of integrating innovative technology into everyday home appliances.
The period from 2020 to the present at LG
The beginning of 2021 presented LG with some unpleasant moments. The phone manufacturing company had been making losses for several years in a row. LG decided to stop producing phones, which happened in 2021. By the way, LG made two attempts to produce tablets. But unsuccessfully – their tablets did not gain popularity. In this decade, LG will upgrade some of its factories, paying more attention to automating assembly processes. LG’s electric car battery business is also doing well. As users, we know that LG makes TVs, home appliances, air conditioners, and laptops.