Samsung has established itself as a dominant force in the Android smartphone arena. Amidst escalating competition and the rise of numerous viable alternatives, Samsung continues to reign supreme. The centerpiece of their dominance is the Galaxy S series, renowned for featuring some of the most advanced and highly-regarded smartphones on the market.
The journey to this eminent position has been a blend of triumphs and challenges for Samsung. From early successes to ventures that sparked debate, the company has navigated through various phases of innovation and experimentation. This exploration into the development of Samsung’s flagship Galaxy S series offers a glimpse into the strategic moves and technological advancements that have shaped their current standing. We examine this evolution to understand how Samsung has continuously adapted and influenced the ever-changing landscape of smartphones.
What is Samsung’s flagship series?
The Galaxy S series is the primary contender when defining Samsung’s flagship smartphone series. It’s worth noting, however, the existence of the Galaxy Z series, which some might also consider flagship material. The Galaxy Z line represents Samsung’s foray into experimental, foldable smartphones. Equipped with top-tier hardware, these devices boast innovation but have a significant price tag, catering to a more niche market. Given the specialized nature of foldable phones, it’s fair to say they don’t quite match the broad appeal of the Galaxy S series. Therefore, we will focus on the Galaxy S series, Samsung’s mainstream flagship line, targeting a wider consumer base.
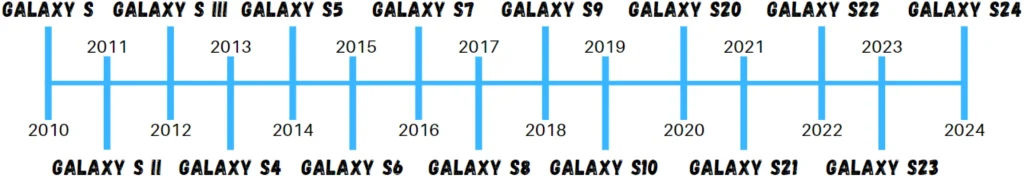
The Galaxy S series embarked on its journey in 2010 and has since unveiled 15 base models. In a strategy reminiscent of Apple’s approach, Samsung launched two or three models simultaneously in each generation. Examples include the S24 and the S24 Ultra, adding to the overall count of variants in the series. Let’s take a closer look at the evolution of this series, starting from its inception.
Samsung Galaxy S

The inaugural model of the Samsung Galaxy S series, often referred to as the Samsung Galaxy S or Galaxy S1, marked a significant milestone in Samsung’s journey in the smartphone market. Released in June 2010, this model signified Samsung’s entry into the arena of “premium” Android smartphones.
The Galaxy S1 was emblematic of the Android smartphones of its time. It boasted an 800 x 480 Super AMOLED display, notable for its clarity and color reproduction. The device was powered by a 1GHz single-core processor accompanied by 500MB of RAM, which, at the time, was sufficient for smartphone users’ demands. For photography, it featured a dual-camera setup, with a 5-megapixel main camera and a modest 0.3-megapixel front-facing camera.
Running on Android 2.1, which later received an update to Android 2.3, the Galaxy S1 also introduced users to Samsung’s custom interface, TouchWiz. While TouchWiz had been a part of previous Samsung smartphones, it found a more refined and user-friendly implementation in the Galaxy S.
Compared to its contemporary, the iPhone 4, the Galaxy S1 offered features that were typical yet popular among Android smartphones at the time, such as a MicroSD slot for memory expansion and a removable battery.

The Samsung Galaxy S saw a unique variation when carriers like Sprint and T-Mobile introduced enhanced versions of the original Samsung Galaxy S, equipped with a built-in QWERTY slide-out keyboard (picture above). However, this experimentation with form factors in the Galaxy S series was short-lived, as Samsung did not continue with such design variations in the subsequent models of the S series.
Samsung Galaxy S II

The Samsung Galaxy S II, unveiled in May 2011, served as the direct successor to the Samsung Galaxy S1, bringing with it a series of incremental but impactful improvements. This sequel maintained the design ethos of its predecessor but introduced some key enhancements.
One of the noticeable changes was in the display. The Galaxy S II expanded its screen size from the original 4 inches to 4.3 inches, although it retained the same resolution. Under the hood, the device received a significant boost in performance with a new 1.2GHz dual-core processor paired with an increased 750MB of RAM.
The camera system also saw notable advancements. The rear camera was upgraded to 8 megapixels, while the front camera was enhanced to 2 megapixels, ensuring better image quality and more detailed selfies. Initially, the Galaxy S II shipped with Android 2.3, but it wasn’t long before it received an update to Android 4.1. This update was accompanied by the TouchWiz 4.0 interface, a refined version of the interface from the original Galaxy S.
While the Galaxy S II was considered a modest upgrade in terms of technological leaps, it achieved remarkable commercial success. The smartphone sold an impressive 40 million units globally, including a rapid sale of 3 million units within the first 55 days of its release. This level of popularity was exceptional for its time, demonstrating Samsung’s growing influence and reputation in the tech world.
Samsung Galaxy S III
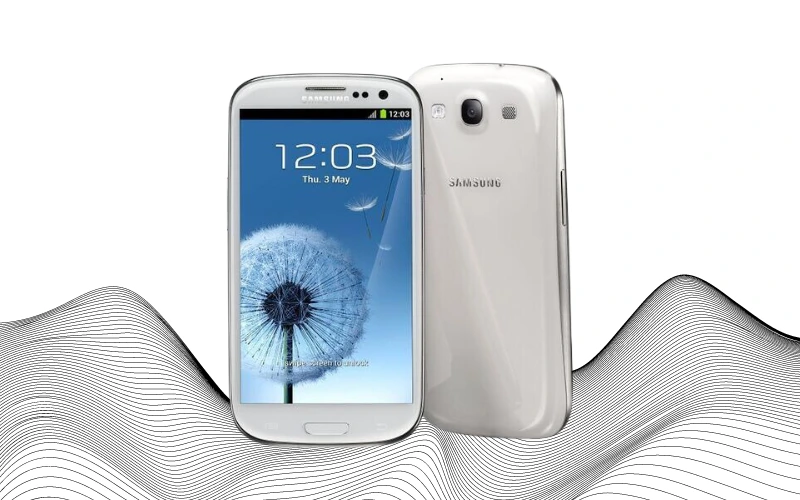

In 2012, Samsung unveiled the Galaxy S III, widely regarded as one of its most aesthetically pleasing smartphones. The launch slogan, “Designed for humans, inspired by nature,” encapsulated the essence of its design philosophy, emphasizing a more organic, user-friendly approach. The Galaxy S III’s design was notably smoother and more rounded than its predecessors.
A standout feature of the Galaxy S III was its large 4.8-inch screen. At the time of its release, such a screen size was considered quite substantial, pushing the boundaries of smartphone display dimensions. Coupled with an HD resolution of 720×1280, it was one of the earliest smartphones to offer such a large, high-quality display, setting a new standard for mobile screen real estate and clarity.
The Galaxy S III also marked the series’s introduction of 4G capabilities. It was equipped with 1GB of RAM and boasted an improved processor, enhancing the overall performance and user experience. Regarding camera technology, Samsung opted to maintain the same specifications for the main camera but upgraded the front camera to support HD video recording. Running on Android 4.0.4 “Ice Cream Sandwich” at launch, the device later received an update to Android 4.3 “Jelly Bean”.
The Galaxy S III’s impact on the market was profound. It achieved phenomenal commercial success, with over 80 million units sold. This remarkable sales figure cemented the Galaxy S III’s position as the second-best-selling Android smartphone in history.
Samsung Galaxy S4

The Samsung Galaxy S4, launched in May 2013, holds the record as the most-sold Android smartphone in history. With over 80 million devices sold, including an astounding 20 million in the first two months, the Galaxy S4’s market impact was monumental. It debuted in a sweeping 155 countries and was available through 327 mobile operators, indicating its massive global reach.
The Galaxy S4 stood out from its predecessor with several key enhancements. It featured a 5-inch Full HD screen. Performance-wise, it was equipped with a robust 1.9GHz quad-core CPU and 2GB of RAM.
Photography capabilities also received a boost, with the rear camera upgraded to 13 megapixels. Notably, the front camera on the Galaxy S4 could record 1080p video, a first for the Galaxy S series. Design-wise, the S4 saw a slight alteration from the S III, and interestingly, it was with this model that Samsung shifted away from using Roman numerals for naming.
Another innovative feature of the Galaxy S4 was wireless charging, marking the series’ foray into this convenient charging technology. The smartphone initially ran on Android 4.2.2 and later received an update to Android 5.0.1, “Lollipop.”
The Galaxy S4’s immense popularity and sales success represented a significant milestone for Samsung.
Samsung Galaxy S5
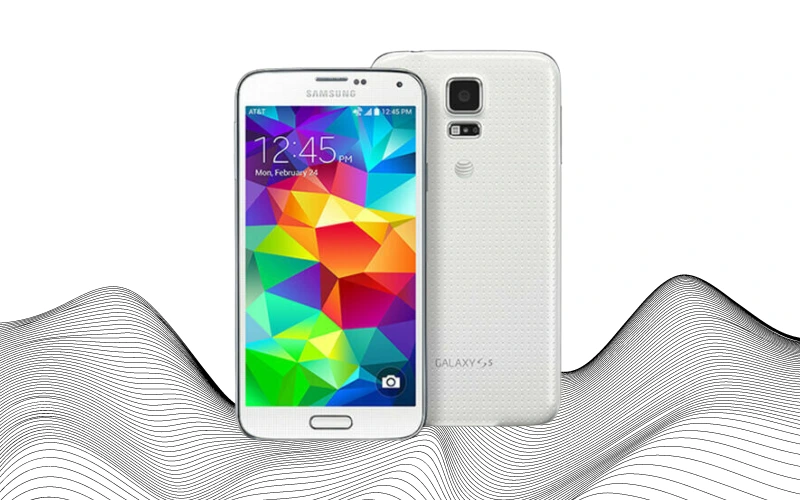

The Samsung Galaxy S5, released in April 2014, faced the daunting task of outdoing the immense success of the Galaxy S4. While it introduced several notable features, it didn’t quite match the popularity of its predecessor. The S5 was a direct improvement over the S4, featuring a redesigned textured back cover that gave it a unique look and feel.
One of the key additions to the S5 was the introduction of a fingerprint scanner integrated into the Home button, enhancing the device’s security. Samsung also improved the device’s water resistance, achieving an IP67 rating, a notable feature for a phone that still offered a removable battery.
The Galaxy S5 positioned itself as a “sporty” smartphone. In later versions, Samsung enhanced the screen resolution to an impressive 2,560 x 1,440 pixels. In another aspect, this model was a trailblazer – it was the first smartphone to utilize a Snapdragon 800-series chip, marking a significant leap in processing power.
The front camera received a major upgrade to 16MP for photography enthusiasts, ensuring high-quality images. Moreover, Samsung integrated a heart rate sensor into the back cover, allowing users to monitor their pulse through the S Health app. This is a step towards integrating health and fitness tracking into smartphones.
Despite these advancements, the Galaxy S5 didn’t achieve the same level of commercial success as its predecessors, with sales figures of around 25 million units. While it was a solid smartphone with several innovative features, it couldn’t replicate the market impact of the earlier models in the Galaxy S series.
Samsung Galaxy S6
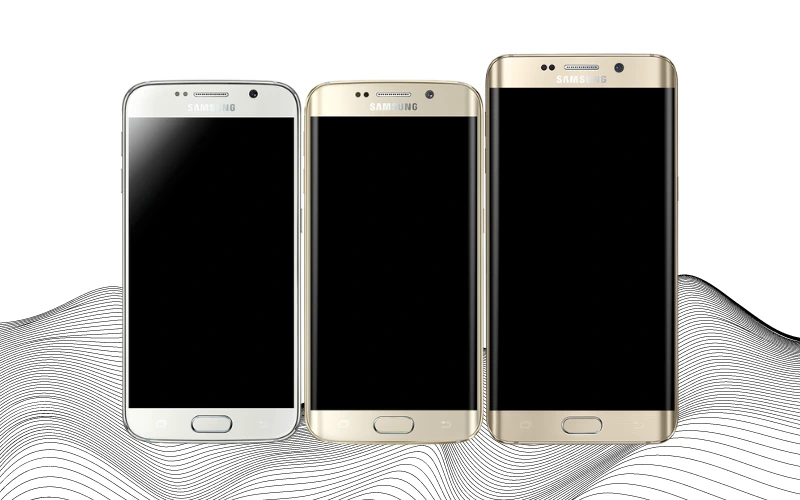

In 2015, with the launch of the Samsung Galaxy S6, Samsung began releasing multiple flagship devices within a single generation. This year marked the debut of the Samsung Galaxy S6 and the Galaxy S6 Edge. The primary distinction between these two models lies in their design and screen shape. The Galaxy S6 Edge boasted curved edges on its screen, a design innovation that made the device more distinctive and more fragile and $100 more expensive. These curved edges allowed Samsung to introduce new features like additional menus and unique gesture controls.
Despite these design differences, the two smartphones shared identical hardware specifications. They were powered by a Quad-core 2.1 GHz Cortex-A57 processor and equipped with 3GB of RAM. The camera system also received a significant upgrade, featuring optical stabilization and the capability to shoot in 4K at 30fps or 1080p at 60fps.
A notable change with these models was the departure from the removable back cover and battery. This design shift meant users could no longer easily replace the battery, marking a change in the Galaxy S series’ design philosophy.
Samsung also introduced the S6 Edge+, essentially an upscaled version of the S6 Edge. It boasted a slightly better processor, a larger battery, and a bigger 5.7-inch screen compared to the 5.1-inch screens of the standard models. Beyond these enhancements, the S6 Edge+ shared many similarities with its smaller counterparts.
All these smartphones initially came with Android 5.0, based on TouchWiz 5.0, and later received updates to Android 7.0 with Samsung Experience 8.0.
Samsung Galaxy S7
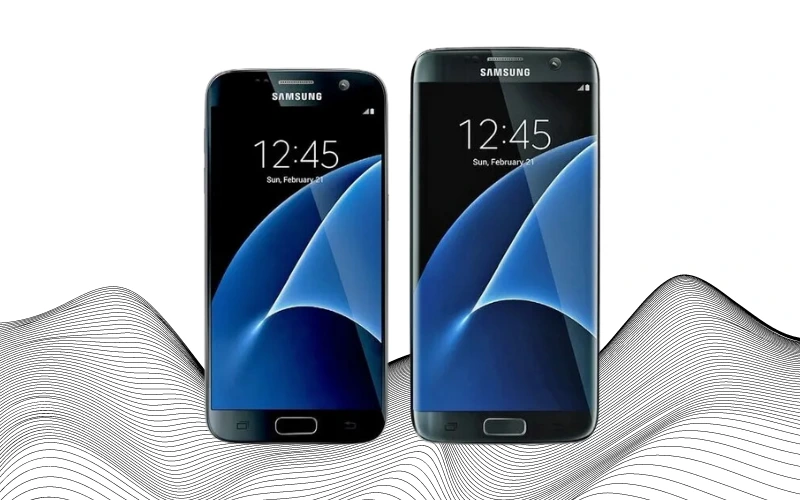

In March 2016, Samsung released the Galaxy S7 in three versions: the standard Galaxy S7, the Galaxy S7 Edge, and the Galaxy S7 Active. The S7 Active boasted an enlarged battery, while the S7 Edge featured a slightly larger screen with curved edges. The standard S7 came with a 5.1-inch screen, and the Edge version offered a 5.5-inch Quad HD Super AMOLED display, sporting a resolution of 2560×1440 pixels. Battery capacity varied between models, with the S7 having a 3,000mAh battery and the S7 Edge a larger 3,700mAh one.
These models represented modest updates over their predecessors and were the last to include the TouchWiz 6.0 interface before transitioning to Samsung Experience.
Samsung also began using different processors in different regions for these models. The European Galaxy S7 came with Samsung’s own Exynos 8890 processor, while the versions sold in China and the USA featured the Qualcomm Snapdragon 820. This led to a period when American and Chinese versions of the Galaxy smartphones had more powerful processors than those in other regions.
Notably, Samsung introduced NFC (Near Field Communication) and launched Samsung Pay with the Galaxy S7, enabling users to make payments directly from their smartphones. Additionally, this generation marked the removal of the IR Blaster. The Galaxy S7 series exceeded 55 million devices in sales, showcasing its popularity and the continued success of Samsung’s flagship line.
Samsung Galaxy S8
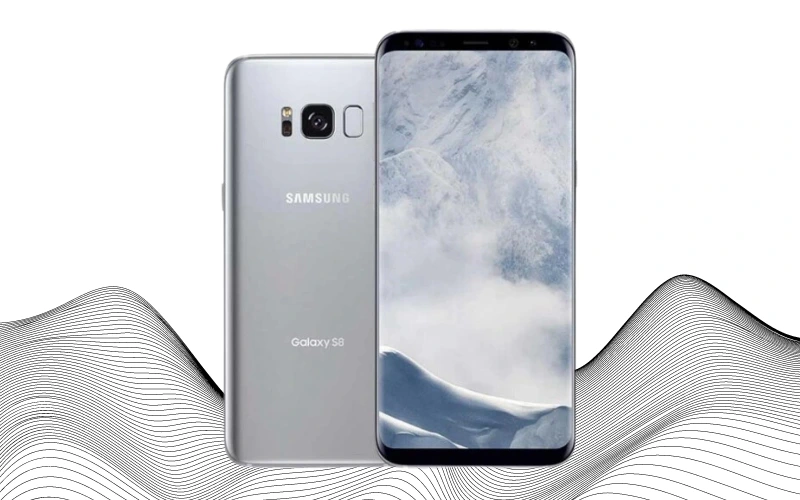

In March 2017, Samsung introduced the Galaxy S8 with a significant design overhaul. They eliminated the physical home button, adopting a sleek, buttonless front. This change led to the relocation of the fingerprint scanner to the back of the phone, next to the camera—a move that received mixed reactions from users. The Galaxy S8 series initially consisted of the standard Galaxy S8 and the larger Galaxy S8+. Later, Samsung added the Galaxy S8 Active, featuring a more robust design and a larger battery.
A notable design feature in both the S8 and S8+ was the curved edges on their screens. The primary differences between these two models were in screen size and battery capacity. The S8 featured a 5.8-inch display with a 3000 mAh battery, while the S8+ boasted a larger 6.2-inch screen with a 3500 mAh battery. Apart from these variations, the devices were identical, each sporting a 2960×1440 1440p Super AMOLED capacitive touchscreen display.
Samsung introduced the Bixby voice assistant with the Galaxy S8, positioning it as a competitor to Apple’s Siri. The S8 models even included a dedicated Bixby button below the volume controls. Camera capabilities improved slightly, including adding a new Pro Mode for enhanced photography options.
The Galaxy S8 series initially came with Samsung Experience 8.1 based on Android 7.0. However, these models were the first to receive an update to the modern One UI Version 1.0
Samsung Galaxy S9
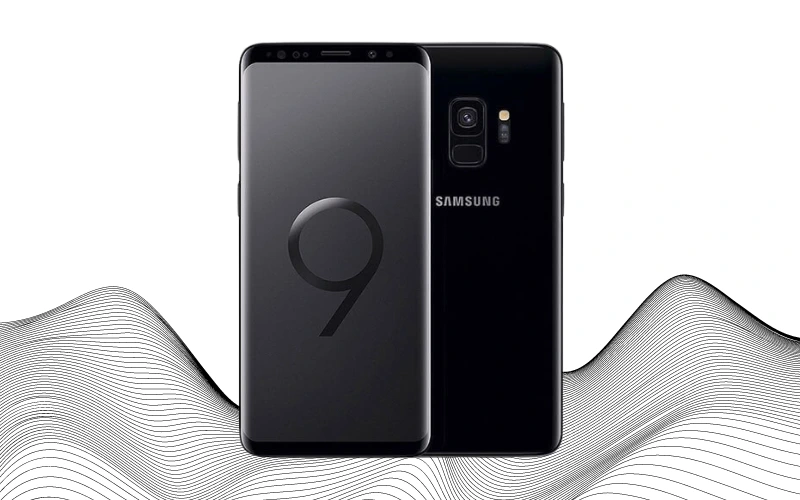

The Samsung Galaxy S9, introduced in 2018, represented a subtle yet focused update to the S8. With this release, Samsung didn’t venture into many new features; instead, they chose to refine and improve upon the existing framework established by the S8. The Galaxy S9 was available in the standard Galaxy S9 and the larger Galaxy S9+. Both models retained their predecessors’ screen sizes and battery capacities, but they introduced fast charging, enhancing the user experience with quicker power-ups.
Samsung’s approach with the S9 was largely about addressing and improving the aspects of the S8. They enhanced the durability of the screen and repositioned the fingerprint sensor to a more user-friendly location, responding to feedback from S8 users. Camera capabilities saw minor improvements, ensuring better photo quality.
Additionally, the Galaxy S9 brought in a new feature for creating animated emojis, akin to Apple’s Animoji, tapping into the growing trend of personalized, animated expressions in digital communication.
Samsung Galaxy S10
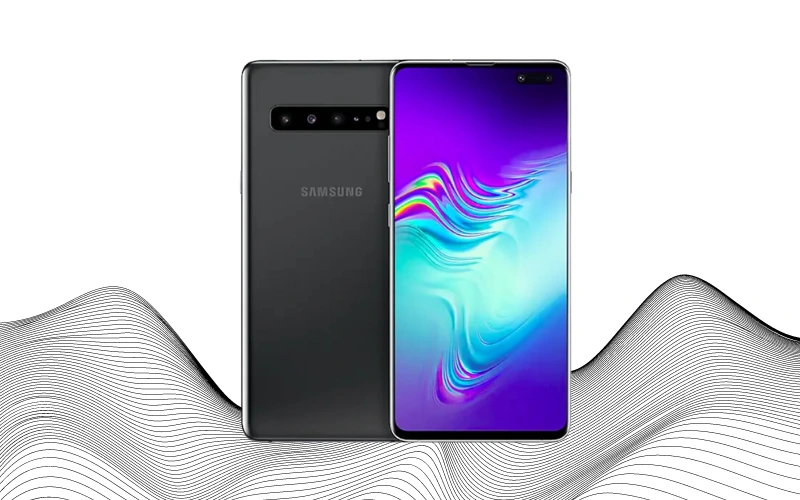

The Samsung Galaxy S10 series, unveiled in 2019, marked another significant leap for Samsung, featuring a diverse lineup: the Galaxy S10e, Galaxy S10, Galaxy S10+, and the Galaxy S10 5G. These models varied in size and performance, with display sizes of 5.8-inch, 6.1-inch, 6.4-inch, and 6.7-inch, respectively. True to its name, the Galaxy S10 5G supported the emerging 5G network technology.
Samsung’s design focus this time was on minimizing bezels. The top and bottom bezels were reduced to thin strips, and the camera was neatly integrated into the screen with a distinctive hole-punch design at the top right corner. The rear cameras received significant upgrades too. The S10e featured two camera modules—a regular and a wide-angle lens—while the S10 and S10+ included three, adding a telephoto lens. The S10 5G model even boasted an ultra-wide camera. This era marked fierce competition between Samsung and Apple, particularly in the race to offer the best camera capabilities.
A novel feature introduced with the S10 series was reverse wireless charging, allowing the phone to charge other devices wirelessly. Waterproofing also improved, and the device transitioned to a fast USB-C port. The fingerprint scanner was ingeniously integrated under the screen, becoming a staple for unlocking Samsung smartphones.
Another first for the Galaxy series was the introduction of a hybrid SIM slot, giving users the option to use either dual SIM cards or a combination of one SIM card and an SD memory card.
The Galaxy S10 series also debuted with the new One UI interface, a significant overhaul from previous Samsung interfaces, focusing on ease of use and a more streamlined user experience. This interface continues to be a key feature in modern Samsung smartphones.
The Galaxy S10 series, with its array of innovations and improvements, stood out as one of the most noteworthy and exciting releases from Samsung in a long while
Samsung Galaxy S20
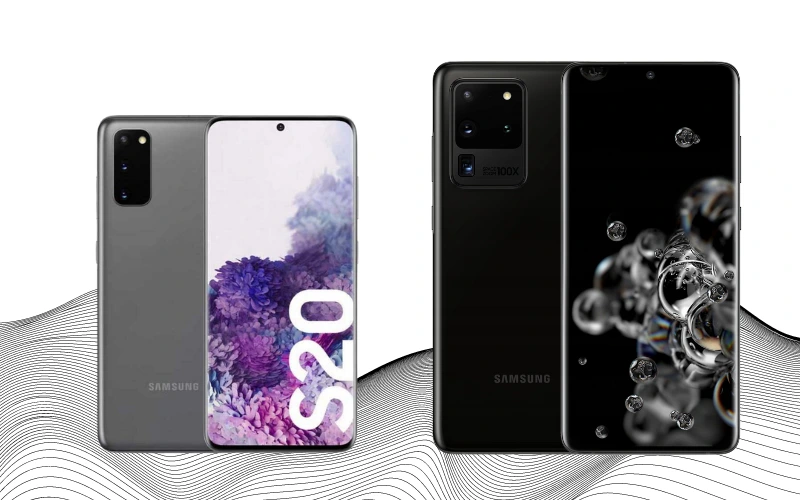

In 2020, Samsung made a notable shift in the naming convention for their flagship smartphones, introducing the Samsung Galaxy S20 and aligning the model name with the year of release. The S20 was launched in four variants: the Samsung Galaxy S20 FE (Fan Edition), which came later as a more affordable version of the S20, the standard Samsung Galaxy S20, the S20+, and the high-end Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra.
Samsung continued to refine its bezel-less design in the S20 series. They positioned the front camera in the center, reducing the top and bottom bezels. The curved screen design was retained. A key enhancement in this generation was introducing a 120Hz display, offering a noticeably smoother experience compared to previous Samsung screens. Notably, they eliminated the 3.5 mm headphone jack and introduced eSIM technology. Fast charging capabilities were also improved, now supporting up to 45 watts.
The S20 and S20+ shared many features, with the main differences being the S20+’s larger battery and screen size (6.2 inches for the S20 and 6.7 inches for the S20+). The Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra stood out with its 6.9-inch screen and advanced camera system. It featured a remarkable 108MP main camera and a 48MP periscope telephoto sensor, capable of up to 100x digital zoom. Additionally, the Ultra model offered enhanced video recording capabilities, supporting 8K resolution at 24 FPS.
Samsung Galaxy S21
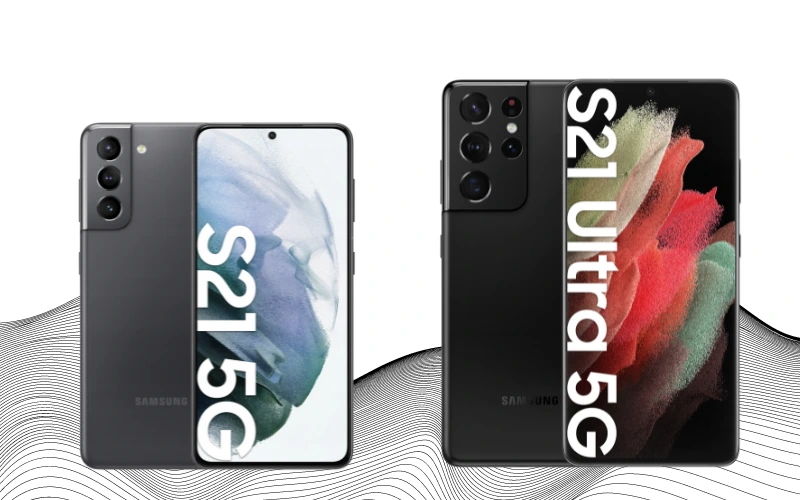

In 2021, Samsung unveiled the Samsung Galaxy S21 series, consisting of the Galaxy S21, Galaxy S21+, and Galaxy S21 Ultra. While these models retained a design and size similar to their predecessors, there were notable changes, particularly in materials and camera design. The back cover of these models was made of plastic instead of glass, and the camera setup shifted from a single block to several separate lenses.
A significant change in the Galaxy S21 series was the screen resolution. Samsung downgraded the displays to 1080p from the previous 1440p but introduced an adaptive refresh rate ranging between 48Hz to 120Hz, optimizing battery usage and screen performance.
The release also marked some removals: the box no longer included a charger and no SD card slot, which aligned with industry trends and caused user dissatisfaction.
However, the Galaxy S21 series brought new features. Notably, the S21 Ultra supported the S Pen stylus, a feature traditionally associated with the Galaxy Note series. The Ultra model also boasted improved optical zoom capabilities, offering 3x and 10x zoom. A point of contention arose with Samsung’s claim that the S21 Ultra could capture detailed photos of the moon. Users found that the phone’s AI was enhancing these images, leading to some debate over the authenticity of the feature.
Despite these controversies and changes, the Galaxy S21 series delivered typical upgrades expected from a new generation of smartphones: faster performance, more detailed cameras, and improved software. This release continued Samsung’s trend of balancing innovation with practicality in their flagship smartphone line.
Samsung Galaxy S22
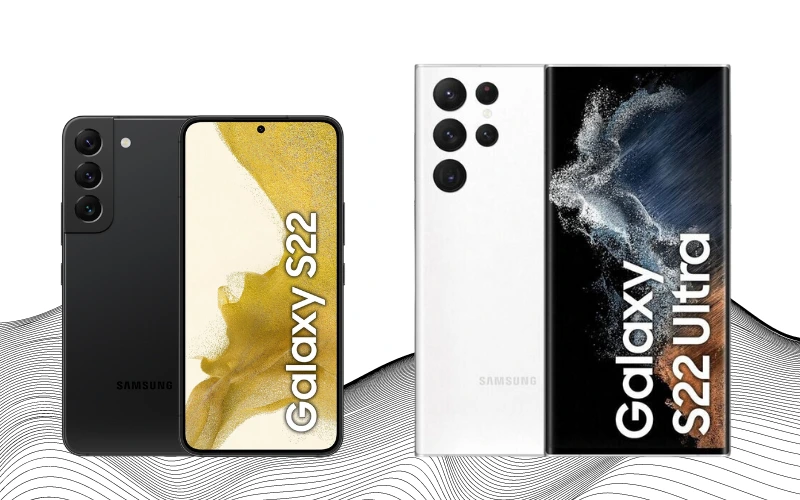

The Samsung Galaxy S22 series, comprising the standard S22, S22+, and S22 Ultra, represented a modest evolution from the previous S21 line. While the overall design remained largely consistent with its predecessor, Samsung made subtle changes to give the S22 Ultra a more rectangular shape.
A significant development in the S22 series was the integration of a built-in S Pen in the S22 Ultra. This feature marked a strategic shift for Samsung, as the discontinuation of the Note series positioned the Galaxy S Ultra as its spiritual successor. The inclusion of the S Pen in the S22 Ultra underscored Samsung’s commitment to catering to users who favored the productivity and creativity tools offered by the stylus.
Beyond these design tweaks, the S22 series strongly resembled the S21 models. The updates included new processors, which offered enhanced performance, increased options for built-in and RAM storage, improved software, and a slightly revised design for the back cover.
The S22 series didn’t present a significant incentive to upgrade for users who already owned an S21. The incremental changes focused more on refining the existing features rather than introducing groundbreaking new ones.
Samsung Galaxy S23
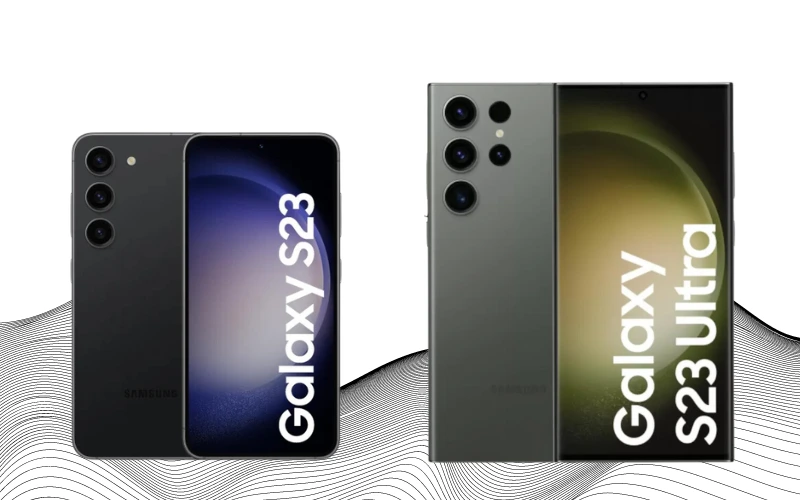

In 2023, Samsung maintained a strategy of incremental updates with the release of the Samsung Galaxy S23 series, including the Galaxy S23, Galaxy S23+, and Galaxy S23 Ultra. These models showcased designs, sizes, and battery performance similar to their S22 predecessors, with no significant changes to the screen technology.
A standout feature of the Galaxy S23 series, particularly in the S23 Ultra, was the introduction of a 200MP camera. This remarkable advancement in camera resolution represented a significant leap forward in smartphone photography, offering unprecedented detail and clarity in images.
Another key decision by Samsung was to standardize Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 processors across all flagship models. This move eliminated the performance discrepancies between different regional versions of their smartphones, ensuring a uniform experience for all users globally.
The focus for the S23 series was predominantly on enhancing the camera capabilities. Combining the more powerful Snapdragon processor and advanced AI algorithms for photo processing allowed Samsung to improve the photography and videography experience significantly. This emphasis on camera technology reflected the growing importance of high-quality smartphone imaging, catering to casual users and photography enthusiasts.
Samsung Galaxy S24
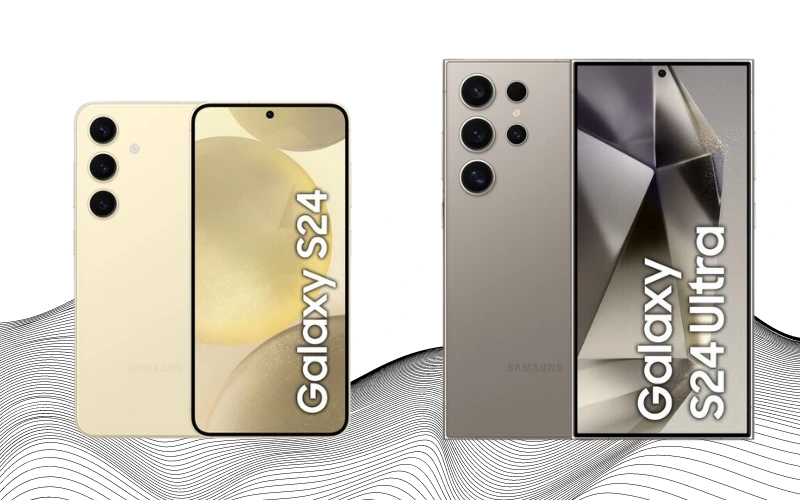

The upcoming Samsung Galaxy S24, announced on January 17, is set to be the latest addition to Samsung’s flagship lineup, though it hasn’t hit the market yet. This model is poised to bring another wave of design innovation. The Galaxy S24 and S24+ will feature aluminum bodies, while the S24 Ultra is set to stand out with a titanium build, suggesting a focus on both aesthetics and durability.
Regarding camera technology, Samsung has chosen to replace the 10x zoom with a 5x zoom, possibly prioritizing image quality over extreme magnification. The Galaxy S24 series is also expected to boast the strongest glass and the new Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 processor. Enhanced video capabilities, such as 4K recording at 120fps and a peak screen brightness of 2600 nits, are among the other notable improvements.
The most captivating feature of the Galaxy S24 series lies in its AI capabilities. This includes real-time translation for calls in text and audio formats, object recognition through photos, an integrated chatbot, and much more, indicating a significant leap in smart features.
From the original Galaxy S in 2010 to the forthcoming Galaxy S24, Samsung’s journey in the flagship smartphone arena reflects a constant push towards technological advancement, user experience improvement, and design innovation, securing its place as a key player in the global smartphone industry.